Advantages of FDM 3D Printing, Do You Know?
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a popular 3D printing technology known for its versatility, affordability, and ease of use. This method has revolutionized the way we approach manufacturing and prototyping, offering numerous benefits that make it an attractive choice for a wide range of applications. In this article, we’ll explore the key advantages of FDM 3D printing and why it continues to be a preferred method for both hobbyists and professionals.
1. Cost-Effectiveness
Affordable Equipment
One of the most significant advantages of FDM 3D printing is its cost-effectiveness. FDM printers are generally more affordable than other types of 3D printers, such as Stereolithography (SLA) or Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) machines. This affordability makes FDM accessible to a broader audience, from hobbyists and educators to small businesses and startups.
Low Material Costs
The cost of filament, the material used in FDM printing, is relatively low compared to the resins used in SLA or the powders used in SLS. This makes it economical to produce prototypes, small batch productions, or even custom items without breaking the bank.
2. Ease of Use
User-Friendly Technology
FDM 3D printers are designed to be user-friendly, with many models offering plug-and-play functionality. This ease of use makes FDM an excellent choice for beginners who are just getting started with 3D printing. The straightforward operation of FDM printers reduces the learning curve, allowing users to focus on their designs rather than complex machine setups.
Wide Availability of Resources
The widespread adoption of FDM technology means there is a wealth of resources available for users. Whether you need tutorials, troubleshooting tips, or design inspiration, there are countless online communities, forums, and guides dedicated to helping you succeed with FDM printing.
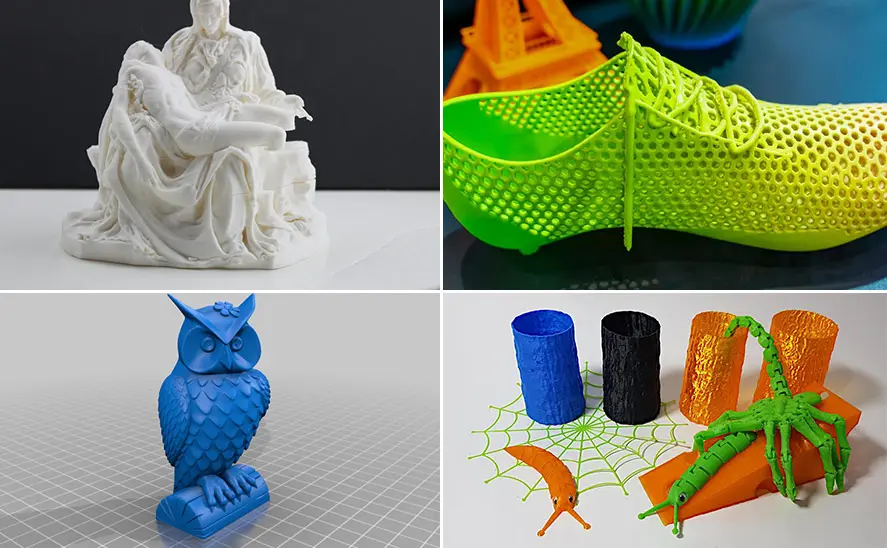

3d prints
3. Material Versatility
Variety of Filaments
FDM technology supports a wide range of materials, each with its unique properties. Common filaments include PLA (Polylactic Acid), ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol), and TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane). These materials cater to different needs, from creating durable, functional parts to flexible or biodegradable objects.
Specialty Filaments
Beyond standard materials, FDM printers can also use specialty filaments, such as carbon fiber-reinforced, wood-filled, or metal-infused filaments. These specialty filaments expand the possibilities for what you can create, making FDM suitable for a wide range of applications, from artistic projects to high-strength engineering components.
4. Rapid Prototyping
Fast Turnaround Time
FDM 3D printing is ideal for rapid prototyping, allowing designers and engineers to quickly turn their ideas into tangible objects. The ability to iterate designs rapidly reduces the time to market and enables faster decision-making in the development process.
Cost-Effective Prototyping
Because of its low material and equipment costs, FDM printing is an economical way to produce prototypes. This affordability means that multiple iterations of a design can be printed and tested without incurring significant expenses, making it easier to refine and perfect a product before moving on to mass production.
5. Scalability
From Desktop to Industrial Scale
FDM technology is highly scalable, with printers available in a range of sizes. Desktop FDM printers are perfect for hobbyists and small businesses, while larger, industrial-grade machines can handle mass production. This scalability makes FDM a viable option for both small and large projects.
Adaptability
FDM printers can be used for various purposes, from creating small, intricate parts to producing larger objects. This adaptability makes FDM technology suitable for a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, healthcare, and consumer products.
6. Environmental Benefits
Biodegradable Filaments
One of the environmental advantages of FDM 3D printing is the use of biodegradable filaments like PLA. Made from renewable resources such as cornstarch, PLA is an eco-friendly material that reduces the environmental impact of 3D printing. This makes FDM a more sustainable option compared to other manufacturing methods that rely on non-renewable resources.
Reduced Waste
FDM 3D printing is an additive manufacturing process, meaning it builds objects layer by layer, using only the material necessary to create the part. This reduces waste compared to subtractive manufacturing methods, such as milling or cutting, where excess material is often discarded.
7. Customization and Flexibility
Personalization
FDM 3D printing allows for easy customization, enabling the creation of personalized objects tailored to individual needs. Whether it’s custom-fit components, bespoke products, or one-of-a-kind designs, FDM technology makes it possible to produce unique items without the need for expensive molds or tooling.
Design Flexibility
The layer-by-layer nature of FDM printing allows for the creation of complex geometries and intricate designs that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. This design flexibility opens up new possibilities for innovation and creativity.
8. Maintenance and Upgradability
Ease of Maintenance
FDM printers are generally easy to maintain, with many components being user-replaceable. Routine maintenance, such as cleaning the nozzle or replacing the build plate, can be performed without specialized knowledge or tools. This ease of maintenance ensures that the printer remains in good working condition, reducing downtime and extending the machine’s lifespan.
Upgradability
Many FDM printers are modular, allowing users to upgrade or customize their machines with add-ons such as improved extruders, heated beds, or enclosure kits. This upgradability ensures that the printer can evolve with the user’s needs, providing a cost-effective way to enhance capabilities without purchasing a new machine.
FDM 3D printing offers a range of advantages that make it a versatile and accessible technology for a wide variety of applications. From its cost-effectiveness and ease of use to its material versatility and scalability, FDM continues to be a leading choice for 3D printing enthusiasts and professionals alike. Whether you’re looking to create prototypes, custom products, or functional parts, FDM technology provides the tools and flexibility needed to bring your ideas to life.
Related:
Everything You Need to Know About FDM 3D Printers
Exploring FDM 3D Printer Technology





